更新时间:2022-08-25 来源:黑马程序员 浏览量:
目录
- [Spring的Async注解线程池扩展方案]
- [目录]
- [1. 扩展目的]
- [2. 扩展实现]
- [2.1 扩展Async注解的执行拦截器`AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`]
- [2.2 扩展Async注解的Spring代理顾问`AsyncAnnotationAdvisor`]
- [2.3 扩展Async注解的 Spring Bean 后置处理器`AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`]
- [2.4 扩展代理异步配置类`ProxyAsyncConfiguration`]
- [2.5 扩展异步代理配置选择器`AsyncConfigurationSelector`]
- [2.6 扩展异步启动注解`@EnableAsync`]
- [3. 额外扩展:给`@Async`注解代理指定线程池]
扩展目的
1. 异步调用,改用Spring提供的`@Aysnc`注解实现,代替手写线程池执行。
2. 在实际场景中,可能会遇到需要将主线程的一些个性化参数、变量、数据传递到子线程中使用的需求。
3. `InheritableThreadLocal`可以解决子线程继承父线程值的需求,但是它存在一些问题。
1. `SessionUser.SESSION_USER`是中台提供,无法修改。
2. `InheritableThreadLocal`在线程池机制应用中并不友好,不及时在子线程中清除的话,会造成线程安全问题。
实现思路有两种:
1. 针对`ThreadLocal`进行扩展,并说服中台统一改用扩展后的`ThreadLocal`。
2. 针对`@EnableAsync`和`@Async`注解进行扩展,将手动copy的代码写入到Spring代理类中。
第一种要跟中台打交道,就很烦,能够天平自己独立解决,就自己解决。第二种会是一个不错的选择,扩展实现也并不困难。
2. 扩展实现
2.1 扩展Async注解的执行拦截器`AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`
类全名:`org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`
从调试记录可以分析得出`AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor#invoke`方法,正是创建异步任务并且执行异步任务的核心代码所在,我们要做的就是重写这个方法,将父线程的运行参数手动copy到子线程任务体中。
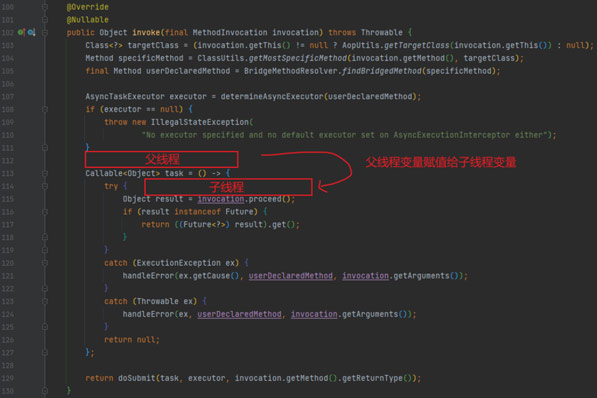
2.2 扩展Async注解的Spring代理顾问`AsyncAnnotationAdvisor`
我们依靠追踪`AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`的构造方法调用,定位到了它。
全类名:`org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncAnnotationAdvisor`
> 补充说明:代理顾问(`Advisor`)、建议(`Advice`)以及Spring代理实现原理
>
> Spring `@EnableAsync`默认的代理模式是 JDK 代理,代理机制如下:
>
> Spring 一个 Bean 会在 `BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization()`这个生命周期环节,遍历所有的`BeanPostProcessor`实例,判断Bean是否符合代理条件,如果符合代理条件,就给 Bean 代理对象中追加建议(`Advice`)对象,这样就完成了代理。
>
> 而建议(`Advice`)对象是由顾问(`Advisor`)对象创建和提供。
>
> 上一小节提到的异步执行拦截器`AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`就是实现了`Advice`接口的类。
在`@Async`注解的代理过程中,异步执行拦截器`AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`就是通过`AsyncAnnotationAdvisor#buildAdvice`方法创建的。
所以,当我们想要将扩展的新的异步执行拦截器`LibraAnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor`用起来,则需要相应的,还要把`AsyncAnnotationAdvisor#buildAdvice`方法重写。
2.3 扩展Async注解的 Spring Bean 后置处理器`AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`
我们依靠追踪`AsyncAnnotationAdvisor`的构造方法调用,定位到了它。
类全名:`org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`
这个没什么好说的,Spring Bean 的生命周期其中一环。是 Spring Bean 实现代理的起点。
开发人员可以自定义一个`BeanPostProcessor`类,把它注册到 Bean 容器中,它就会自动生效,并将后续的每一个 Bean 实例进行条件判断以及进行代理。
我们要重写的方法是:`AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#setBeanFactory`。这个方法构造了异步代理顾问`AsyncAnnotationAdvisor`对象。
2.4 扩展代理异步配置类`ProxyAsyncConfiguration`
`AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`不是一般的 Spring Bean。它有几个限制,导致它不能直接通过`@Component`或者`@Configuration`来创建实例。
`AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`仅仅是实现了基于 JDK 代理,如果开发决定另外一种(基于ASPECTJ编织),那么它就应该受到某种条件判断来进行 Bean 实例化。
2. `AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor`还需要配置指定的线程池、排序等等属性,所以无法直接使用`@Component`注解注册为 Bean。
我们阅读一下`@EnableAsync`注解源码:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAsync {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
```进一步阅读`AsyncConfigurationSelector`的源码:
public class AsyncConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableAsync> {
private static final String ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME =
"org.springframework.scheduling.aspectj.AspectJAsyncConfiguration";
/**
* 分别为EnableAsync.mode()的PROXY和ASPECTJ值返回{@link ProxyAsyncConfiguration}或{@code AspectJAsyncConfiguration} 。
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
default:
return null;
}
}
}
``` 谜底揭晓,`ProxyAsyncConfiguration`原来是在这里开始注册到 Spring 容器中的。
Spring Boot 启动后,会根据`@EnableAsync`注解的`mode()`方法的具体值,来决定整个Spring的 Bean 代理机制。
既然 Spring 代理机制只会有一种,所以,也就只会在两种机制的配置类中选择其中一个来进行实例化。
而默认`EnableAsync$mode()`默认值是`AdviceMode.PROXY`,所以默认采用 JDK 代理机制。
2.5 扩展异步代理配置选择器`AsyncConfigurationSelector`
类全名:`org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurationSelector`
2.6 扩展异步启动注解`@EnableAsync`
类全名:`org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync`
3. 额外扩展:给`@Async`注解代理指定线程池
`@Async`会自动根据类型`TaskExecutor.class`从 Spring Bean 容器中找一个已经实例化的异步任务执行器(线程池)。如果找不到,则另寻他路,尝试从 Spring Bean 容器中查找名称为`taskExecutor`的`Executor.class`实例。最后都还是未找到呢,就默认自动`new`一个`SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor`来用。
> 补充说明:`TaskExecutor.class`是Spring定义的,而`Executor.class`JDK定义的。
场景:其他小伙伴、或者旧代码已经实现过了一个线程池,但是这个线程池,是个`Executor.class`类型,且 Bean 实例名称不是`taskExecutor`(假设是`libraThreadPool`),正常情况下`@Async`根本无法找到它。
需求:通过配置,将`@Async`的默认线程池,指定为名为`libraThreadPool`的`Executor.class`类型线程池。
我们只需要注册一个实现`AsyncConfigurer`接口的配置类
`org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AbstractAsyncConfiguration#setConfigurers`:
/**
* Collect any {@link AsyncConfigurer} beans through autowiring.
*/
@Autowired(required = false)
void setConfigurers(Collection<AsyncConfigurer> configurers) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
return;
}
if (configurers.size() > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Only one AsyncConfigurer may exist");
}
AsyncConfigurer configurer = configurers.iterator().next();
this.executor = configurer::getAsyncExecutor;
this.exceptionHandler = configurer::getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
}
```AI鸿蒙原生智能正式版课程,培养全端跨平台鸿蒙工程师
2026-03-10AI鸿蒙原生智能正式版课程,培养全端跨平台鸿蒙工程师
2026-03-10毕业16个工作日,平均薪资13180元,就业率100%,广州黑马AI智能应用开发(Java)学科20250529班
2026-03-06毕业32个工作日,平均薪资11147元,就业率95%,广州黑马AI智能应用开发(Java)学科20250326班
2026-03-05黑马程序员2025全国就业数据发布:全学科平均就业率92.07%,AI开发类就业平均薪资达11869.67元。
2026-03-05黑马全国校区齐开班!场面太太太壮观了!
2026-03-03